Main Menu
- Home
- Products
- Applications
- Product Support
- Service
- Learn
- Product News
- About Us
- Contact Us
Noise Criteria (NC) and Room Criteria (RC) curves are two related tools to evaluate and specify acceptable levels of indoor ambient broad-spectrum noise (often called background noise. Typically, this noise comes from internal sources, including building mechanical systems like HVAC, but external sources, like road noise are also considered.
Background noise that is too loud or annoying can not only interfere with speech intelligibility, it can also be a source of fatigue that can have a negative effect on safety and productivity.
It is common in new construction for businesses, education, and government to specify the maximum allowed level of background noise in a room using an NC or RC level. Both Noise Criteria and Room Criteria are specified by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) in the standard ANSI/ASA S12.2-2019: Criteria For Evaluating Room Noise.
An NC or RC level is a single number metric that characterizes the background noise in a room. Room Criteria measurements include additional parameters described later.
NC Curves were plots of SPL vs frequency first developed in the 1950s based on surveys of acceptable noise level. They can be thought of as equal perceived loudness contours. Room Criteria curves, first proposed in the 1980s, aimed to improve on NC curves by taking into account a subjective understanding of the character of the sound or sound quality. While NC curves were most focused on speech intelligibility over background noise, the developers of RC curves also wanted to ensure that background noise did not have annoying characteristic like high frequency hiss or low frequency rumble that would not be flagged by the NC rating.
In both cases, a sound level meter plots background noise levels over a range of frequencies using 1/1 octave band Leq, compare that plot to the established NC or RC curves, and provide an NC or RC level or rating. So, how is this level determined? In short, the NC or RC level is defined by the highest curve that the measured sound in any octave band reaches. Even if the Leq measurements for every other octave band are lower, this single touch point determines the NC rating In the example below, the measured result does not go above the NC 24 curve, so the NC level is 24.
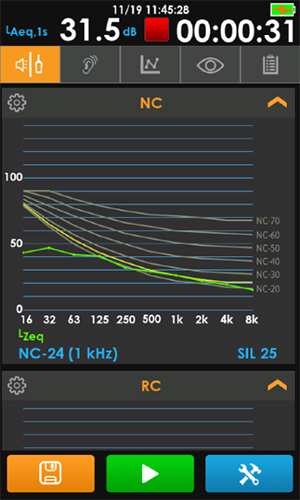 This method of determining NC Rating is know as the tangency method.
This method of determining NC Rating is know as the tangency method.
An alternative method for approximating the NC rating uses Speech Interference Level (SIL) rounded to the nearest dB noted as NC-(SIL). The SoundExpert meter computes and reports the SIL level using the following formula.
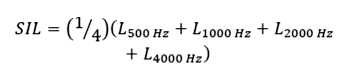
The RC rating has two parts: a numerical rating known as LMF and additional designations.
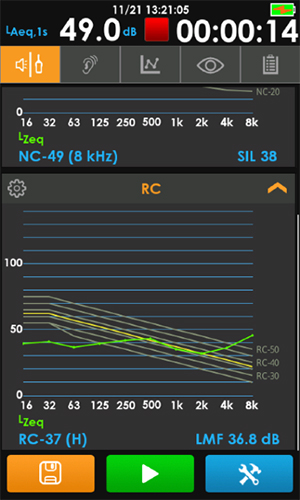 Example of a room with hiss.
Example of a room with hiss.
| Recording Studio | NC 15-20 |
| Quiet Office or Home Environment | NC 25-30 |
| Hospital, Hotel, or Classroom | NC 30-35 |
| Retail Store | NC 40-45 |
Note that a similar set of curves known as Noise Rating Curves were developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). NR Curves are most commonly used outside of North America. It is important to understand whether you are measuring NC or NR, as each method will produce different results (for example, NC 30 is not equivalent to NR 30). Larson Davis Sound Level Meters that offer NC/RC include the ability to measure according to Noise Rating Curves as well.